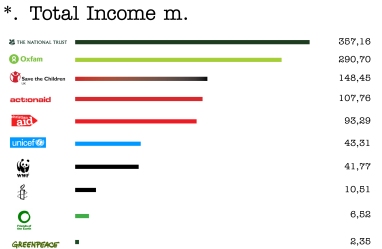Filed under: History | Tags: Arts, branding, brands, charity, design, volunteering, young people

Amnesty International (AI) is an independent, non-profit organization, which protects and campaigns for the Human Rights. It is a worldwide movement of ordinary people who help ordinary people.
AI was founded in 1961 by Peter Benenson, an English lawyer who established an article, called “The Forgotten Prisoners”, in The Observer Newspaper. The reason that this article was written by him, was the imprisonment of two Portuguese students, because they raised their glasses of wine in a toast to freedom.

Peter (Solomon) Benenson was born in 1921. His father, Harold Solomon, was a brigadier-general in the First World War and his mother Flora Solomon (Benenson) was the daughter of Grigory Benenson, Russian-Jewish banker in Russia. Benenson lost his father when he was 9 years old, by an accident. After that he had a privately tutor, W.H Auden. Then he studied history in Eton College and in the Oxford University, but the Second World War was the reason to interrupt his studies and to join the military. His Russian background was a basic factor that navy rejected him. During his military service, Benenson studied law and he focused on human rights. In 1946 he joined the Labour Party and he was the leader in the society of Labour Lawyers. Through Labour Party, Benenson had different activities relevant to human rights, which in 1948 was established the Universal Declaration of Human Rights. He was observer in different trials, as in 1956 the “Treason Trial” of Nelson Mandela.
His activities merged when he was 15 years old, when he organized support for the Spanish Relief Committee. In the same time he adopted one baby of himself and he tried to help Jews from Nazi. He raised 4.000 pounds to bring two German Jews in Britain.
In 1960 Benenson read the article about the two Portuguese students and this was the time that Amnesty was born. But Benenson wasnt alone. It was a committee included Benenson, Eric Baker, Louis Blom-Cooper, Peggy Crane and Peter Archer. The two of them were playing a basic role in this project.
Luis Blom-Cooper is a English author and lawyer. He is the person who had a basic role in “The Observer” newspaper and who suggested Benenson to write this article.
Eric Baker was the second important person of the idea “Appeal Amnesty 1961”. Benenson met Eric Baker in Cyprus between 1950 – 60. Baker was a human rights activist and during this period he made four peace missions in Cyprus. His meetings with Benenson were crucial and important for their future. Baker was the person who create the term “Prisoner of conscience” and which was the main idea which used by the Amnesty.
So in 1961 Amnesty International was founded and in the same year delegates from France, Ireland, UK, USA, Belgium and Switzerland met in Luxembourg to establish the international movement.
Also Benenson asked from Diana Redhouse, an English artist, to design the Amnesty’s logo. The inspiration was by the Chinese proverb…”better to light a candle than to curse the darkness”….The result is the candle in barbed wired…

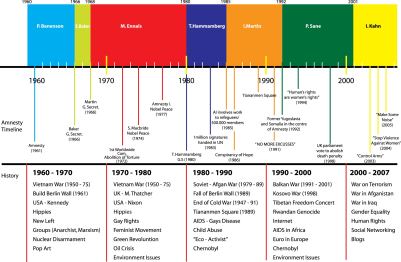
In this stage it is important to research the historical context of Amnesty and what were the historical, political and social events this period.
1960 – 1969
- Vietnam War
- Build Berlin Wall
- USA – Kennedy
- Hippies
- New Left – Socialism
- Nuclear Disarmament
- Pop Art
Amnesty Timeline (1960 – 69):
- 1964 – Benenson called “President”
- 1966 – Benenson left Amnesty and Baker was the 1st General Secretary
- 1968 – Martin Ennals was the 2nd General Secretary (1968 – 1980)
Martin Ennals was an human rights activist. He was the person who changed the perception of Amnesty. Before he was General Secretary, AI had 7 staff and 17.000 pounds annual income. Next year there were 150 staff and 2 millions pounds annual income. When Ennals was General Secretary in AI, Amnesty won the Nobel Prize Award in 1977 and the UN Human Rights Award 1978. He tried to make an strong campaign organization.
1970 – 1979
- Vietnam War
- UK – M. Thatcher
- USA – Nixon
- Hippies
- Gay Rights
- Feminist Movement
- Green Revoluntion
- Oil Crisis
- Environment Issues
Amnesty Timeline (1970 -79) :
- 1st Worldwide campaign – Abolish Torture (1972)
- Sean Macbride won the Nobel Prize (1974)
- AI won the Nobel Prize Award (1977)
- AI won the UN Human Rights Award 1978
1980 – 1989
- Soviet – Afgan War
- Fall of Berlin Wall
- End of Cold War
- Tiananmen Square
- AIDS – Gays Disease
- Child Abuse
- Chernobyl
- “Eco – Activist”
Amnesty Timeline (1980 – 89)
- Thomas Hammamberg General Secretary (1980 – 85)
- 1 million signatures handed in UN
- AI involves work to refugees. 500.000 members (1985)
- “Conspiracy of hope” (1986)
- Tiananmen Square (1989)
T. Hammamberg is a Swedish Diplomat and human rights activist. He was a General Secretary in Amnesty in 1980 to 1985. Before this he was a teacher and journalist in Sweden (1969 – 79). He was Chairman of the International Execute Committee in AI (1976 – 79)
1990 – 1999
- Balkan War
- Kosovo War
- Tibetan Freedom
- Rwandan Genocide
- Internet
- AIDS in Africa
- Euro in Europe
Amnesty Timeline (1990 – 99)
- Ian Martin – General Secretary (1986 – 92)
- Pierre Sane – General Secretary (1992 – 2001)
- Former Yugoslavia and Somalia were in the center of AI campaigns
- “NO MORE EXCUSES”
- “Human’s rights are women’s rights
- UK parliament voted to abolish death penalty
Ian Martin is an English human rights activist. Representative UN in Nepal
Pierre Sane was the Secretary General in AI. He born in Dakar and he studied Political Science at Carleton University and MBA in Bordeaux in France. During his time in AI he reorganized the whole view and strategy of the organization. His most important activities were:
- World Conference of Universal Declaration of Human Rights
- World Conference on Women in Beijing
- 50th Anniversary of UDHR
Also he led some famous and successful for the Amnesty campaigns:
- Women’s rights
- Human Rights Defender’s
- Socio-economic and cultural rights
- abolition of torture and death penalty
2000 – 2007
- War on Terrorism (11 Sep. 2001)
- War in Afghanistan
- War in Iraq
- Gender equality
- Social Networking
- Blogs
Amnesty Timeline (2000 – 07)
- Control Arms
- Irene Khan – Secretary General (2001 – present)
- Stop Violence Against Women
- Make Some Noise
Irene Khan is the 1ts women Secretary in AI. She is Bangladeshi and she studied law at the Victoria University of Manchester and in USA in Harvard Law School. She helped to create Concern Universal and she became human rights activist in 1979 with International Commission of Jurist.
AMNESTY STRUCTURE
- Peter Benenson ( 1961 – 1966) – President
- Eric Baker (1966 – 1968 – Secretary General
- Martin Ennals (1968 – 1980) – Secretary General
- Thomas Hammamberg (1980 – 1985) – Secretary General
- Ian Martin (1986 -1991) – Secretary General
- Pierre Sane (1992 – 2001) – Secretary General
- Irene Khan (2001 – Present) – Secretary General
Filed under: N.P.D, N.P.D - Audience | Tags: Arts, branding, brands, charity, design, volunteering
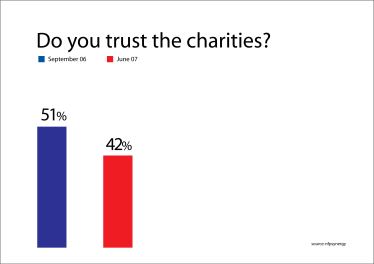
The magazine Third Sector in 26th of March 2008, was published a survey about the trust of the charities. It is an annual survey of 1.000. The results of this survey shows that people trust the charities less than the previous year. Especially it is dropped 9% down than the previous year. That means that 2 in 5 adults trust the charities.
Also in the most positive group is young people (16-25), who trust charities and they believe that charities can change something in the future.
Filed under: N.P.D | Tags: Arts, branding, brands, charity, design, volunteering, young people
When you start to define your territory is the first view to understand what happen in this area… What is the product, the competitors, the audience… Everything which be relevant to your territory… The research is the first stage to realize your area and to start thinking what maybe is the problem, or better the gap in this market…
I strongly believe that all the markets have “gaps” and this is the only way to go on, to adopt the trends and to development their profiles… The most common mistake is to define what is the “gap”… The only way to succeed is to look deep in your research… The answer is in your hands but you have to be rational and to look objectively the informations that you have already collect…
In my area, “charities in UK”, I collect many informations like financial reports, annual reports and social demographic statistics, which all of them describe with numbers this territory… When I evaluated more these informations, more and more questions were born in my mind… And this is the point…If you have a questions and you need an answer, you are in a correct road to find a gap and to try to fill it… Some of my questions are: Why people prefer to donate than to be volunteer? Why they prefer to give money in medical research than in human rights? Why young people are the lowest group which take attention in charities (donation and volunteering)?
So the result of these questions is that I found a gap in this area:
Young people (16-24) they dont give so much attention about charities….like the other age groups? But WHY???
Giving Money: It is obviously that young people are not employers, and if they have money they prefer to spend them in different interests (food, clothes, entertainment…)
Volunteering: Young people dont volunteer because:
NOT
- dont have enough time
- bureaucracy
- dont have the essential informations (poor communication)
- worried about the risks
- dont get the right skills
- they feel that charities are not well-organized
- wouldn’t be able to stop once get involved
- volunteer is becoming too much like paid work
Why young people prefer to volunteer?
YES
- help people
- cause is important for me
- learn new skills
- enchaining their employment prospects
- meet new friends
- satisfaction about the last result
- better position in the community
So…Combine them and look what the young people want????
Your audience has the answer…listen them!!!